VBA Lesson 29: Combo Boxes in VBA for Excel
This is an excerpt from Pierre Leclerc (www.excel-vba.com)
Before we begin on the Combo Box
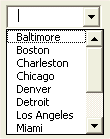
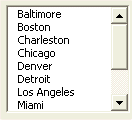
The difference between a combo box and a list box is that the combo box is a drop-down list and the user can submit a single value from the drop-down list. The list box shows a certain number of values with or without a scroll bar and the user can select one or more values.
|
Combo Box |
List Box |
If you are looking for a drop-down list (also called pull-down lists) to use on a regular worksheet see the much easier and user friendly Excel drop-down lists in the website on Excel.
When you double click on the combo box in the Visual Basic Editor you will see all its properties in the Properties window .
No programming is needed to submit the list of values that will be offered to the user within the combo box. Look for the RowSource property.
The RowSource Property:
The values that should appear in the drop-down list of the combo box are submitted in the RowSource property. For example, if the value of the RowSource property is Balance!A1:A12 The values residing in cell A1 to A12 of the sheet named Balance will be offered as choices to the user who clicks on the small arrow of the combo box.
The rules to submit the RowSource property is the name of the sheet where the list resides followed by an exclamation point (!), the address of the first cell, a colon and the address of the last cell.
IMPORTANT NOTE: if there is a space or a special character within the name of the sheet where the list resides you must surround it with simple quotes. For example: 'New Balance'!A1:A12.

 Back home
Back home